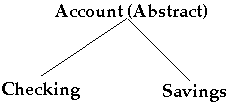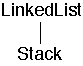| CS 535: Object-Oriented Programming & Design |
|
|---|
Fall Semester, 1997
Doc 12, Inheritance & Polymorphism
To Lecture Notes Index
San Diego State University -- This page last updated 05-Oct-97
Contents of Doc 12, Inheritance & Polymorphism
- References
- Inheritance and Polymorphism
- Simplistic Example
- Finding Classes
- Relationships Between Classes
- Is-kind-of, is-a, is-a-type-of
- is-analogous-to
- is-part-of or has-a
- Banking Classes
R. J. Abbott, "Programming Design by Informal English Descriptions",
Communications of the ACM, Vol. 26, No 11, November 1983, pp. 882 -
894
Grady Booch, Object-Oriented Analysis and Design, 1994
Mark Lorenz, Object-Oriented Software Development: A Practical Guide,
1993, Appendix I Measures and Metrics
Johnson, Ralph E. and Foote, Brain, "Designing Reusable Classes," Journal of
Object-Oriented Programming, pages 22-35, June/July 1988.
Shlaer, S. and Mellor, S.J., Object-Oriented Systems Analysis: Modeling the
World In Data, Yourdon Press: Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey,
1988.
Last Federal Virtual Bank wants its entire banking software redone in Java, so
it can shut down its branch offices and perform all its business via the WWW.
Customer records include the customers name, address, personal information,
passwords, etc. and accounts.
The bank offers various types of accounts: checking, savings, CD, Junior
savings accounts.
Bank officers will introduce new types of accounts from time to time.
Checking account charge 12 cents/check unless the average account balance for
the month is greater than $1,000. The first three ATM transactions per month
are free. Additional ATM transactions cost 50 cents.
All transactions over $1,000 dollars must be reported to the federal
government.
Junior savings accounts are for children under the age of 13. Children can
deposit any amount into the account. Deposits of over $100 are reported to
their parents. Children can withdrawal up to $10 from the account. Individual
withdrawals over $10 must be verified by a parent. Total withdrawals over $100
per month are reported to the parents.
Transactions include time & date, amount, location, type of transaction,
account number and teller.
Abbot[1]
"In an English description of the problem, the nouns are candidates for
objects; the verbs are candidates for operations."
Look at these phrases. Some will be obvious classes, some will be obvious
nonsense, and some will fall between obvious and nonsense. Skip the nonsense,
keep the rest. The goal is a list of candidate objects. Some items in the
list will be eliminated, others will be added later. Finding good objects is a
skill, like finding a good functional decomposition.
Booch[2]
"The tangible things in problem domain, the roles they play, and the events
that may occur form the candidate classes and object of our design."
- Disks
- Printers Airplanes
- Model conceptual entities that form a cohesive abstraction
- Window
- File Bank Account
- If more than one word applies to a concept select the one that is most
meaningful
- Model categories of classes
- Categories may become abstract classes
-
- Keep them as individual classes at this point
- Model known interfaces to outside world
- User interfaces
-
- Interfaces to other programs
-
- Model the values of attributes, not the attributes themselves
- Height of a rectangle
Height is an attribute of rectangle
Value of height is a number
Rectangle can record its height
Finding Classes Other Views
Coad and Yourdon
Structure
-
- "Kind of" and "part of" relationships
Other systems
-
- External systems with which the application interacts
Devices
-
- Devices with which the application interacts
Events remembered
-
- Historical event that must be recorded
Roles played
-
- Different roles users play in interacting with application
Locations
-
- Physical locations, offices and sites important to the application
Ross
People
-
- Humans who carry out some function
- Farmers
Places
-
- Areas set aside for people or things
-
- Fields on farm
Things
- Physical objects or groups of objects
-
- Plants
- leaves roots
Organizations
- Formally organized collections of people, resources, facilities
-
- Union
- farm crew
Concepts
- Principles or ideas not tangible
Events
- Things that happen
Shaler & Mellor[3]
Tangible things
-
- Cars
- telemetry data
Roles
-
- Mother
- teacher
Events
-
- Landing
- interrupt
Interactions
-
- Loan
- meeting
Is-kind-of or is-a
is-analogous-to
is-part-of or has-a
Is-kind-of, is-a, is-a-type-of
Let A and B be classes
To determine if A should be the parent class of B ask:
- Is B an A ( or is B a type of A, or is B a kind of A)
If the answer is no, then do not A the parent of B
If the answer is yes, then consider making A the parent of B
Example 1 Bank Accounts
A JuniorSavingsAccount is a type of a SavingsAccount
So consider making JuniorSavingsAccount a subclass of SavingsAccount
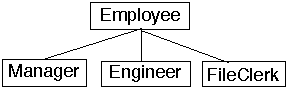
Example 2 Employees
Consider Employee, Manager, Engineer, and FileClerk
A Manager is a kind of an Employee
So should we make Employee a parent class of a Manager class?
Is Manager a class or a role that an Employee object will play?
- Does Manager contain data or operations that Employee does not?
-
- If no, then Manager is likely a role for an Employee object
class Employee { //lots of stuff here not shown }
class Driver
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
Employee manager = new Employee( "Roger" );
Employee fileClerk = new Employee( "Smith" );
}
}
Example 2 Employees - Continued
If Manager, etc are classes then several options:
Option 1 Direct inheritance
-
class Employee
{
// stuff not shown
}
class Manager extends Employee
{
// stuff not shown
}
etc.
Option 2 Separate Inheritance Structure
-
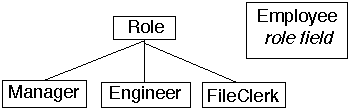
class Employee
{
Role position;
// stuff not shown
}
class Role
{
// stuff not shown
}
class Manager extends Role
{
// stuff not shown
}
If class X is-analogous-to class Y then look for superclass
Example BankAccounts
A checking account is analogous to a saving account
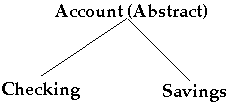
If class A is-part-of class B then there is no inheritance
Some negotiation between A and B for responsibilities may be needed
Example: Linked-List class and a Stack
A stack uses a linked-list in its implementation
A stack has a linked-list
So the Stack class and the LinkedList class are separate classes

class LinkedList
{
public void addFront( Object item) { // not shown}
public Object removeFront() { // not shown}
public Object removeEnd() { // not shown}
}
class Stack
{
LinkedList stackElements = new LinkedList();
public void push( Object item )
{
stackElements.addFront( item);
}
}
A Common Mistake
Using inheritance with a is-part-of (has-a) relation between classes
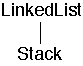
class LinkedList
{
// fields not shown
public void addFront( Object item) { // not shown}
public Object removeFront() { // not shown}
public Object removeEnd() { // not shown}
}
class Stack extends LinkedList
{
public void push( Object item )
{
addFront( item);
}
}
class Test
{
public static void main( String[] arguments)
{
Stack problem = new Stack();
problem.push( "Hi");
problem.push( "Mom" );
problem.removeEnd(); // ????
}
}
Customer
Transaction
Currency
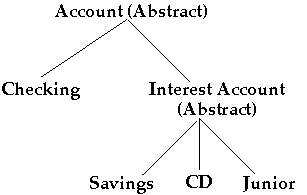
Account
abstract class account {
public static final boolean VALID = true;
protected Customer accountOwner;
protected Currency balance;
protected Stack accountHistory;
// Other fields left out
public void processTransaction( Transaction accountActivity ) {
if ( validateTransaction( accountActivity ) == VALID )
commitTransaction( accountActivity );
else
// report the problem. Code not shown
}
protected abstract boolean validateTransaction( Transaction
accountActivity
);
protected abstract void commitTransaction( Transaction
accountActivity
);
// other methods left out
}
Account Class Inheritance
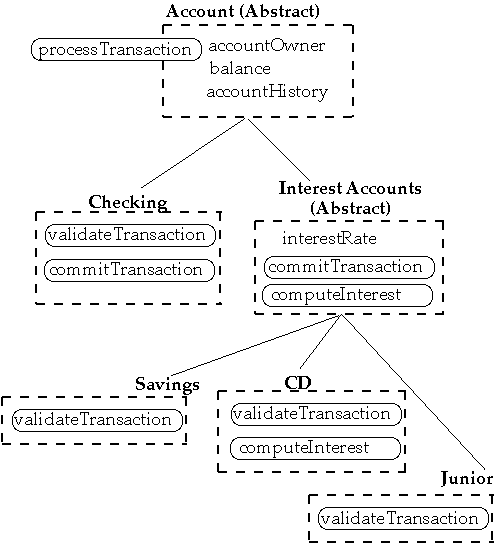
Polymorphism
Account newCustomer;
newCustomer = magicFunctionToCreateNewAccount()
newCustomer.processTransaction( amount );
Which
processTransaction is called?
Adding new types of accounts to program requires:
- Adding new subclasses
-
- Changing code that creates objects