 CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
Fall Semester, 1996
IO & Streams
[To Lecture Notes Index]
San Diego State University -- This page last updated Oct 15, 1996

Contents of IO & Streams
- References
- The I/O Package
- InputStream
- OutputStream
- PrintStream
- FileInputStream
- FileOutputStream
- ASCIIInputStream
- Combining InputStreams
- Combining OutputStreams
- File
- StreamTokenizer
- Some Real Parsing
Core Java, Chapter 11
The Java Programming Language, Arnold and Gosling, Chapter 11
On-line Java Documentation
Java source code
From a programmer's point of view, the user is a peripheral that types when
you issue a read request
- Peter Williams
I/O is defined in terms of streams
Streams are ordered sequences of data that have:
- A source (input streams) or
-
- A destination (output stream)
Streams usually come in pairs input and output
- FileInputStream
-
- FileOutputStream
Streams are designed to be combined
IO Package Classes
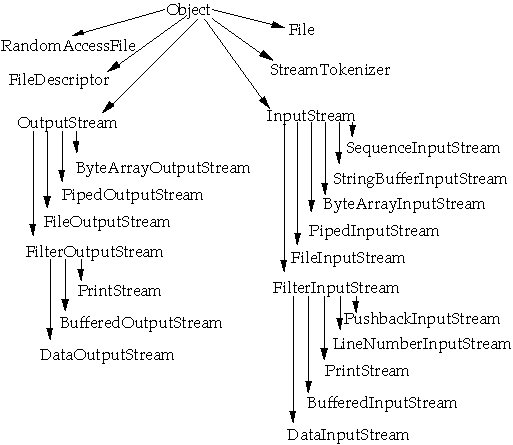 Data Interfaces and Implementors
Data Interfaces and Implementors
Stream Types
Piped Streams
- Useful in communications between threads
ByteArray Streams
- Read/write byte arrays
Filter Streams
- Abstract classes, filter bytes from another stream
- Can be chained together
Buffered Streams
- Adds buffering
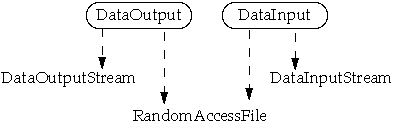
Data Streams
- Reads/writes built-in types (int, float, etc )
- Steam stores types in binary not ASCII or Unicode
File Streams
- Used for file IO
An abstract class representing an input stream of bytes. All InputStreams are
based on this class.
Methods
| available() | read() |
| close() | read(byte[]) |
| mark(int) | read(byte[], int, int) |
| markSupported() | reset() |
| skip(long) |
Description of Methods
available()
- Returns the number of bytes that can be read without blocking.
close()
- Closes the input stream.
mark(int)
- Marks the current position in the input stream.
markSupported()
- Returns a boolean indicating whether or not this stream type supports
mark/reset.
InputStream Continued
read()
- Reads a byte of data, but returns an int
read(byte[])
- Reads into an array of bytes.
read(byte[], int, int)
- Reads into an array of bytes.
reset()
- Repositions the stream to the last marked position.
skip(long)
- Skips n bytes of input.
InputStream Example
class CountSize
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws IOException,
FileNotFoundException
{
try
{
InputStream in = new FileInputStream( "Exam" );
int total;
for ( total = 0; in.read() != -1; total++)
;
System.out.println( total );
}
catch ( FileNotFoundException fileProblem )
{
System.err.println( "File not found" );
throw fileProblem;
}
catch ( IOException ioProblem )
{
System.err.println( "IO problem" );
throw ioProblem;
}
}
}
Output
7428
Read, int and Char
read() returns -1 if end of stream is reached, else returns the next byte
class Read
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws IOException
{
InputStream in
in = new StringBufferInputStream( "abcdefghij" );
System.out.println( in.read() + " raw read, ascii value " );
System.out.println( (char) in.read() + " cast read to char " );
}
}
Output
97 raw read, ascii value
b cast read to char
Abstract class representing an output stream of bytes. All OutputStreams are
based on this class.
Note byte oriented IO works on ascii only, not Unicode
Methods
| close() | write(byte[], int, int) |
| flush() | write(int) |
| write(byte[]) | |
Description of Methods
close()
- Closes the stream
flush()
- Flushes the stream
write(byte[])
- Writes an array of bytes
write(byte[], int, int)
- Writes a sub array of bytes
write(int)
- Writes a byte
OutputStream Example
class CountSize
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws IOException
{
InputStream in;
in = new StringBufferInputStream( "abcdefghij" );
OutputStream out = System.out;
int nextChar;
while ( ( nextChar = in.read() ) != -1 )
out.write( Character.toUpperCase( (char) nextChar ) );
out.write( '\n' );
out.flush();
}
}
Output
ABCDEFGHIJ
Used for "ascii" output
System.out is a PrintStream
class PrintStreamExample
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
System.out.println( "Hi Mom" );
}
}
Constructors
PrintStream(OutputStream)
- Creates a new PrintStream.
PrintStream(OutputStream, boolean)
- Creates a new PrintStream, with auto flushing.
PrintStream Methods
| checkError() | print(int) | println(double) |
| close() | print(long) | println(float) |
| flush() | print(Object) | println(int) |
| print(boolean) | print(String) | println(long) |
| print(char) | println() | println(Object) |
| print(char[]) | println(boolean) | println(String) |
| print(double) | println(char) | write(byte[], int, int) |
| print(float) | println(char[]) | write(int) |
checkError()
- Flushes the print stream and returns whether or not there was an error on
the output stream.
PrintStream, '\n' and auto flush
If auto flushing is on (default) then printing an '\n' flushes the buffer in a
PrintStream
Write in PrintStream
public void write(int b)
{
try
{
out.write(b);
if (autoflush && (b == '\n'))
{
out.flush();
}
}
catch (InterruptedIOException ex)
{
// We've been interrupted. Make sure we're still interrupted.
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
catch (IOException ex)
{
trouble = true;
}
}
The toString() Standard
class PoorPrint
{
String name = "sam";
}
class FancyPrint
{
String name = "pete";
public String toString()
{
return "FancyPrint( " + name + " )";
}
}
class TestPrint
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
PoorPrint outOfIt = new PoorPrint();
FancyPrint cool = new FancyPrint();
System.out.println( outOfIt );
System.out.println( cool );
}
}
Output
PoorPrint@5e300848
FancyPrint( pete )
The toString() StandardHow Does it Work?
Print in PrintStream
public void print( Object obj )
{
print( String.valueOf( obj ) );
}
String.valueOf
public static String valueOf(Object obj)
{
return (obj == null) ? "null" : obj.toString();
}
Constructors
FileInputStream(String)
- Creates an input file with the specified system dependent file name.
FileInputStream(File)
- Creates an input file from the specified File object.
FileInputStream(FileDescriptor)
FileInputStream Methods
| available() | read() |
| close() | read(byte[]) |
| finalize() | read(byte[], int, int) |
| getFD() | skip(long) |
Constructors
FileOutputStream(String)
- Creates an output file with the specified system dependent file name.
FileOutputStream(File)
- Creates an output file with the specified File object.
FileOutputStream(FileDescriptor)
FileOutputStream Methods
| close() | write(byte[]) |
| finalize() | write(byte[], int, int) |
| getFD() | write(int) |
Constructors
ASCIIInputStream(InputStream)
- Creates a new ASCIIInputStream.
ASCIIInputStream Method
| bad() | readChar() | readLong() |
| eof() | readDouble() | readShort() |
| flushLine() | readFloat() | readUnsignedByte() |
| read(byte[]) | readFully(byte[]) | readUnsignedShort() |
| read(byte[], int, int) | readFully(byte[], int, int) | readUTF() |
| readBoolean() | readInt() | readWord() |
| readByte() | readLine() | skipBytes(int) |
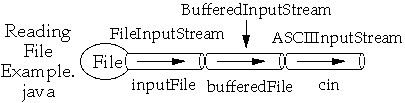
import java.io.*;
import sdsu.io.*;
class ReadingFileExample
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception
{
FileInputStream inputFile;
BufferedInputStream bufferedFile;
ASCIIInputStream cin;
inputFile = new FileInputStream( "ReadingFileExample.java" );
bufferedFile = new BufferedInputStream( inputFile );
cin = new ASCIIInputStream( bufferedFile );
System.out.println( cin.readWord() );
for ( int k = 1 ; k < 4; k++ )
System.out.println( cin.readLine() );
}
}
Output
import
sdsu.io.*;
import java.io.*;
class ReadingFileExample
UpperCaseInputStream Example
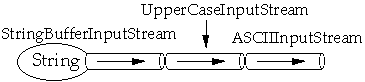
public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception
{
InputStream input;
ASCIIInputStream cin;
input = new StringBufferInputStream( "hi mom how is dad?" );
input = new UpperCaseInputStream( input );
cin = new ASCIIInputStream( input );
System.out.println( cin.readWord() );
System.out.println( cin.readLine() );
Output
HI
MOM HOW IS DAD?
Creating New Streams
class UpperCaseInputStream extends FilterInputStream
{
public static final int EOF = -1;
public UpperCaseInputStream( InputStream input )
{
super( input ); // input is stored in field "in"
}
public int read() throws IOException
{
int nextChar = in.read();
if ( nextChar == EOF )
return EOF;
else
return toUpperCase( (char) nextChar );
}
public int read(byte bytes[], int offset, int length) throws
IOException
{
int charsRead = in.read(bytes, offset, length);
if ( charsRead == EOF )
return EOF;
for ( int index = offset; index < offset + charsRead; index++)
bytes[ index ] = toUpperCase( (char) bytes[ index ] ) ;
return charsRead;
}
protected byte toUpperCase( char convertMe ) {
return (byte) Character.toUpperCase( convertMe );
}
}

import java.io.*;
class WritingToFileExample
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception
{
FileOutputStream outputFile;
BufferedOutputStream bufferedFile;
PrintStream cout;
outputFile = new FileOutputStream( "LetterHome" );
bufferedFile = new BufferedOutputStream( outputFile );
cout = new PrintStream( bufferedFile );
cout.println( "Hi Mom" );
cout.println( "How is Dad?" );
cout.flush();
cout.close();
}
}
Constants
pathSeparator ( unix = : )
The system dependent path separator string.
pathSeparatorChar ( unix = : )
The system dependent path separator character.
separator ( unix = / )
The system dependent file separator String.
separatorChar ( unix = / )
The system dependent file separator character.
Constructors
File(String)
Creates a File object.
File(String, String)
Creates a File object from the specified directory.
File(File, String)
Creates a File object (given a directory File object).
File Methods
| canRead() | getParent() | length() |
| canWrite() | getPath() | list() |
| delete() | hashCode() | list(FilenameFilter) |
| equals(Object) | isAbsolute() | mkdir() |
| exists() | isDirectory() | mkdirs() |
| getAbsolutePath() | isFile() | renameTo(File) |
| getName() | lastModified() | toString() |
File Example
import java.io.*;
class FileExamples {
public static void main( String args[] )
{
// New files
File classDirectory = new File( "cs596" );
classDirectory.mkdir(); // Did not exist prior
File gradeFile = new File( "cs596", "grades.text" );
gradeFile.mkdir(); // Did not exist prior
File lectureNotes = new File( "cs596/lectures.text" );
lectureNotes.mkdir(); // Did not exist prior
// Existing file
File sourceFile = new File( "FileExamples.java" );
String[] fileList = classDirectory.list();
for ( int fileNum = 0; fileNum < fileList.length; fileNum++ )
System.out.print( fileList[ fileNum ] + "\t" );
System.out.println();
System.out.println( classDirectory.getAbsolutePath() );
System.out.println( gradeFile.exists() );
System.out.println( gradeFile.getParent() );
System.out.println( sourceFile.length() );
System.out.println( sourceFile.lastModified() );
gradeFile.delete();
}
}
Output
grades.text lectures.text
/home/ma/whitney/java/notes/cs596
true
cs596
980
823933450000
Directory Example
import java.io.*;
class MakeDirectoriesExamples
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
// Does nothing if test/this does not exist
File a = new File( "test/this/out" );
a.mkdir();
// creates all four directories
File b = new File( "second/test/of/this" );
b.mkdirs();
}
}
import java.io.*;
class MachineIndependentFileNames
{
public static void main( String args[] )
{
String gradeFile = "/home/ma/whitney/cs596/grades";
gradeFile = gradeFile.replace( '/', File.separatorChar );
System.out.println( gradeFile );
}
}
Methods
| commentChar(int) | pushBack() |
| eolIsSignificant(boolean) | quoteChar(int) |
| lineno() | resetSyntax() |
| lowerCaseMode(boolean) | slashSlashComments(boolean) |
| nextToken() | slashStarComments(boolean) |
| ordinaryChar(int) | toString() |
| ordinaryChars(int, int) | whitespaceChars(int, int) |
| parseNumbers() | wordChars(int, int) |
StreamTokenizer
- More complex than the StringTokenizer
- Designed to parse "Java-style" input
- Parses numbers
- Parses Java-style comments
nextToken
Returns the type of the next token
Places token type in field ttype
Places the token in a public field
- sval for string (or word )
- nval for number (declared a double not Double)
Token Types
TT_WORD
-
- A string (word) was scanned
- The string field sval contains the word scanned
TT_NUMBER
-
- A number was scanned
- Only decimal floating-point numbers (with or without a decimal point) are
recognized
TT_EOL
- End-of-line scanned
TT_EOF
- End-of-file scanned
Simple Example
import java.io.*;
class Tokenizer
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception
{
String sample = "this 123 is an 3.14 \n simple test";
InputStream in;
in = new StringBufferInputStream( sample );
StreamTokenizer parser = new StreamTokenizer( in );
while ( parser.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF )
{
if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_WORD)
System.out.println( "A word: " + parser.sval );
else if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_NUMBER )
System.out.println( "A number: " + parser.nval );
else if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_EOL )
System.out.println( "EOL" );
else
System.out.println( "Other: " + (char) parser.ttype );
}
}
}
Output
A word: this
A number: 123
A word: is
A word: an
A number: 3.14
A word: simple
A word: test
Terms and Defaults
Special Characters
- Characters that are treated special
- White space
- Characters that make up numbers
- Characters that make up words (tokens)
Ordinary Characters
- All nonspecial characters
Default Values
Word characters
- a - z
- A - Z
- ascii values 130 through 255
White space
- ascii values 0 through 32
- includes space, tab, line feed, carriage return, escape
comment character /
quote characters " (double quote) ' (single quote )
parse numbers on
Default to OFF
eolIsSignificant are ends of line significant
lowerCaseMode converts all to lower case
slashSlashComments recognize /* */ comments
slashStarComments recognize // comments
Warning
Documentation states:
public void resetSyntax()
Resets the syntax table so that all characters are special.
Source code states:
public void resetSyntax()
Resets the syntax table so that all characters are special.
Source code does:
public void resetSyntax()
Resets the syntax table so that all characters are ordinary.
EOL Example
import java.io.*;
class Tokenizer
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception
{
String sample = "this 123 is an 3.14 \n simple test";
InputStream in = new StringBufferInputStream( sample );
StreamTokenizer parser = new StreamTokenizer( in );
parser.eolIsSignificant( true );
while ( parser.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF )
{
if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_WORD)
System.out.println( "A word: " + parser.sval );
else if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_NUMBER )
System.out.println( "A number: " + parser.nval );
else if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_EOL )
System.out.println( "EOL" );
else
System.out.println( "Other: " + (char) parser.ttype );
}
}
}
Output
A word: this
A number: 123
A word: is
A word: an
A number: 3.14
EOL
A word: simple
A word: test
Default Comment Character
import java.io.*;
class Tokenizer
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception
{
String sample = "this 123 /is an 3.14 \n simple test";
InputStream in = new StringBufferInputStream( sample );
StreamTokenizer parser = new StreamTokenizer( in );
while ( parser.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF )
{
if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_WORD)
System.out.println( "A word: " + parser.sval );
else if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_NUMBER )
System.out.println( "A number: " + parser.nval );
else if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_EOL )
System.out.println( "EOL" );
else
System.out.println( "Other: " + (char) parser.ttype );
}
}
}
Output
A word: this
A number: 123
A word: simple
A word: test
Quote Character
import java.io.*;
class Tokenizer
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception
{
String sample = "this #123 /is an 3.14# \n simple test";
InputStream in = new StringBufferInputStream( sample );
StreamTokenizer parser = new StreamTokenizer( in );
parser.quoteChar( '#' );
while ( parser.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF )
{
if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_WORD)
System.out.println( "A word: " + parser.sval );
else if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_NUMBER )
System.out.println( "A number: " + parser.nval );
else if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_EOL )
System.out.println( "EOL" );
else
System.out.println( "Other: " + (char) parser.ttype +
"sval: " + parser.sval );
}
}
}
Output
A word: this
Other: #sval: 123 /is an 3.14
A word: simple
A word: test
\n always counts between Quote Characters
import java.io.*;
class Tokenizer
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception
{
String sample = "this #123 /is an 3.14 \n simple # test";
InputStream in = new StringBufferInputStream( sample );
StreamTokenizer parser = new StreamTokenizer( in );
parser.quoteChar( '#' );
while ( parser.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF )
{
if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_WORD)
System.out.println( "A word: " + parser.sval );
else if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_NUMBER )
System.out.println( "A number: " + parser.nval );
else if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_EOL )
System.out.println( "EOL" );
else
System.out.println( "Other: " + (char) parser.ttype +
"sval: " + parser.sval );
}
}
}
Output
A word: this
Other: #sval: 123 /is an 3.14
A word: simple
Other: #sval: test
Some Parsing Fun
import java.io.*;
class Tokenizer {
public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception {
String sample = "this #123 /is an 3.14 \n simple # test";
InputStream in = new StringBufferInputStream( sample );
StreamTokenizer parser = new StreamTokenizer( in );
parser.wordChars( 0, 255 );
parser.ordinaryChar( 's' );
while ( parser.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF )
{
if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_WORD)
System.out.println( "A word: " + parser.sval );
else if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_NUMBER )
System.out.println( "A number: " + parser.nval );
else if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_EOL )
System.out.println( "EOL" );
else
System.out.println( "Other: " + (char) parser.ttype +
"sval: " + parser.sval );
}
}
}
Output
A word: thi
Other: ssval: null
A word: #123 /i
Other: ssval: null
A word: an 3.14
Other: ssval: null
A word: imple # te
Other: ssval: null
A word: t
class Tokenizer
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception
{
String sample = "name=value; sam = \n A";
InputStream in = new StringBufferInputStream( sample );
StreamTokenizer parser = new StreamTokenizer( in );
parser.wordChars( 0, 255 );
parser.whitespaceChars( 0, 32 );
parser.ordinaryChar( ';' );
parser.ordinaryChar( '=' );
while ( parser.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF )
{
if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_WORD)
// same as previous examples
}
}
}
Output
A word: name
Other: =sval: null
A word: value
Other: ;sval: null
A word: sam
Other: =sval: null
A word: A
Getting Fancy
class Tokenizer
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception
{
String sample = "name with space=value # a commment\n; "
+ " 'sam =cat' = \n A";
InputStream in = new StringBufferInputStream( sample );
StreamTokenizer parser = new StreamTokenizer( in );
parser.wordChars( 0, 255 );
parser.whitespaceChars( 9, 13 ); //tab, line feed, return
parser.ordinaryChar( ';' );
parser.ordinaryChar( '=' );
parser.commentChar( '#' );
parser.quoteChar( '\'' );
while ( parser.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF )
{
// Same as other examples
}
}
}
Output
A word: name with space
Other: =sval: null
A word: value
Other: ;sval: null
Other: 'sval: sam =cat
Other: =sval: null
A word: A
Toggling
public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception
{
String sample = "name;with;space=value # a commment\n; "
+ "sam & cat = \n A";
InputStream in = new StringBufferInputStream( sample );
StreamTokenizer parser = new StreamTokenizer( in );
parser.wordChars( 0, 255 );
parser.whitespaceChars( 9, 13 ); //tab, line feed, return
parser.ordinaryChar( '=' );
parser.commentChar( '#' );
while ( parser.nextToken() != StreamTokenizer.TT_EOF )
{
if ( parser.ttype == StreamTokenizer.TT_WORD)
System.out.println( "A word: " + parser.sval );
else if ( parser.ttype == '=' )
{
System.out.println( "=: ");
parser.ordinaryChar( ';' );
parser.wordChars( '=', '=' );
}
else if ( parser.ttype == ';' )
{
System.out.println( ";: " );
parser.ordinaryChar( '=' );
parser.wordChars( ';', ';' );
}
else
System.out.println( "Error: " + (char) parser.ttype +
"sval: " + parser.sval );
}
}
Output
A word: name;with;space
=:
A word: value
;:
A word: sam & cat
=:
A word: A
 CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design



