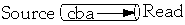CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
Fall Semester, 1996
Doc 15, IO & Streams with pics
[To Lecture Notes Index]
San Diego State University -- This page last updated Oct 17, 1996

Contents of Doc 15, IO & Streams with pics
- References
- The I/O Package
- InputStream
- OutputStream
Core Java, Chapter 11
The Java Programming Language, Arnold and Gosling, Chapter 11
On-line Java Documentation
Java source code
From a programmer's point of view, the user is a peripheral that types when
you issue a read request
- Peter Williams
I/O is defined in terms of streams
Streams are ordered sequences of data that have:
- A source (input streams) or
-
-
- A destination (output stream)
Streams as "Pipes"
- InputStream
-
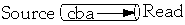
-
- OutputStream
-
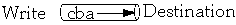
Streams usually come in pairs input and output
- FileInputStream
-
- FileOutputStream
Streams are designed to be combined
-
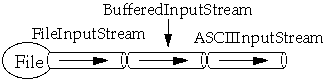
IO Package Classes
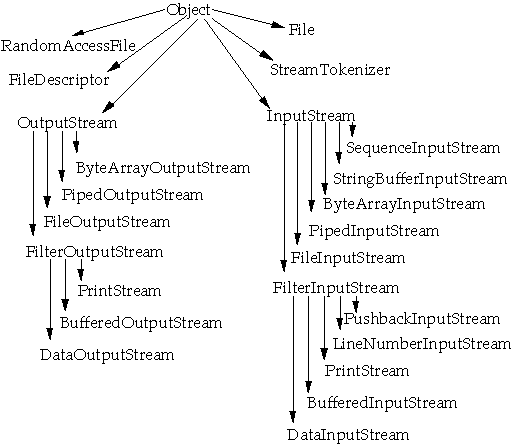 Data Interfaces and Implementors
Data Interfaces and Implementors
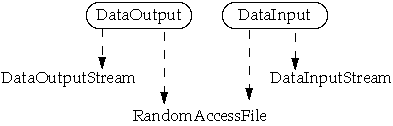
Stream Types
Piped Streams
- Useful in communications between threads
ByteArray Streams
- Read/write byte arrays
Filter Streams
- Abstract classes, filter bytes from another stream
- Can be chained together
Buffered Streams
- Adds buffering
Data Streams
- Reads/writes built-in types (int, float, etc )
- Steam stores types in binary not ASCII or Unicode
File Streams
- Used for file IO
An abstract class representing an input stream of bytes. All InputStreams are
based on this class.
Methods
| available() | read() |
| close() | read(byte[]) |
| mark(int) | read(byte[], int, int) |
| markSupported() | reset() |
| skip(long) |
Description of Methods
available()
- Returns the number of bytes that can be read without blocking.
close()
- Closes the input stream.
mark(int)
- Marks the current position in the input stream.
markSupported()
- Returns a boolean indicating whether or not this stream type supports
mark/reset.
InputStream Continued
read()
- Reads a byte of data, but returns an int
read(byte[])
- Reads into an array of bytes.
read(byte[], int, int)
- Reads into an array of bytes.
reset()
- Repositions the stream to the last marked position.
skip(long)
- Skips n bytes of input.
InputStream Example
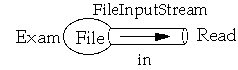
class CountSize
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws IOException,
FileNotFoundException
{
try
{
InputStream in = new FileInputStream( "Exam" );
int total;
for ( total = 0; in.read() != -1; total++)
;
System.out.println( total );
}
catch ( FileNotFoundException fileProblem )
{
System.err.println( "File not found" );
throw fileProblem;
}
catch ( IOException ioProblem )
{
System.err.println( "IO problem" );
throw ioProblem;
}
}
}
Output
7428
Read, int and Char
read() returns -1 if end of stream is reached, else returns the next byte
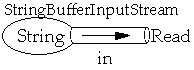
class Read
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws IOException
{
InputStream in
in = new StringBufferInputStream( "abcdefghij" );
System.out.println( in.read() + " raw read, ascii value " );
System.out.println( (char) in.read() + " cast read to char " );
}
}
Output
97 raw read, ascii value
b cast read to char
Abstract class representing an output stream of bytes. All OutputStreams are
based on this class.
Note byte oriented IO works on ascii only, not Unicode
Methods
| close() | write(byte[], int, int) |
| flush() | write(int) |
| write(byte[]) | |
Description of Methods
close()
- Closes the stream
flush()
- Flushes the stream
write(byte[])
- Writes an array of bytes
write(byte[], int, int)
- Writes a sub array of bytes
write(int)
- Writes a byte
OutputStream Example

class CountSize
{
public static void main( String args[] ) throws IOException
{
InputStream in;
in = new StringBufferInputStream( "abcdefghij" );
OutputStream out = System.out;
int nextChar;
while ( ( nextChar = in.read() ) != -1 )
out.write( Character.toUpperCase( (char) nextChar ) );
out.write( '\n' );
out.flush();
}
}
Output
ABCDEFGHIJ
 CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design