 CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & DesignDoc 27 AWT Layouts, Panels, Canvases
 CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
CS535 Object-Oriented Programming & Design
| Button | Label | Scrollbar |
| Canvas | List | TextArea |
| Checkbox | Panel | TextField |
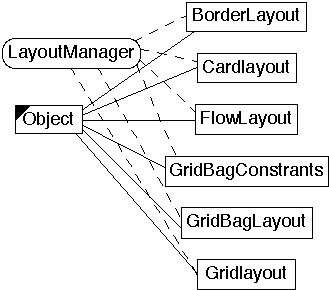
addLayoutComponent(String,Component) layoutContainer(Container) minimumLayoutSize(Container) preferredLayoutSize(Container) removeLayoutComponent(Component) toString()
import java.awt.*;
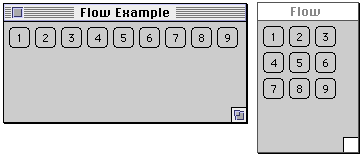
class FlowExample extends Frame {
public FlowExample( int width, int height ) {
setTitle( "Flow Example" );
resize( width, height );
setLayout( new FlowLayout( FlowLayout.LEFT) );
for ( int label = 1; label < 10; label++ )
add( new Button( String.valueOf( label ) ) );
show();
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
new FlowExample( 175, 100 );
new FlowExample( 175, 100 );
}
}
import java.awt.*;
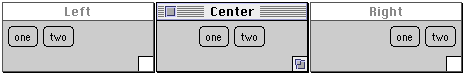
class AlignmentExample extends Frame {
public AlignmentExample( int width, int height,
String title, int alignment ) {
setTitle( title );
resize( width, height );
setLayout( new FlowLayout( alignment) );
add( new Button( "one") );
add( new Button( "two") );
show();
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
new AlignmentExample( 150, 50, "Left", FlowLayout.LEFT);
new AlignmentExample( 150, 50, "Right", FlowLayout.RIGHT);
new AlignmentExample( 150, 50, "Center", FlowLayout.CENTER);
}
}
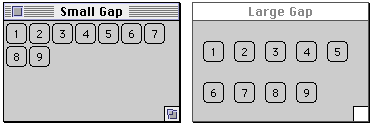
class GapExample extends Frame {
public GapExample( int width, int height, String title,
int HorizontalGap, int VerticalGap ) {
setTitle( title );
resize( width, height );
setLayout( new FlowLayout( FlowLayout.LEFT,
HorizontalGap,VerticalGap) );
for ( int label = 1; label < 10; label++ )
add( new Button( String.valueOf( label ) ) );
show();
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
new GapExample( 175, 100, "Small Gap", 2, 2 );
new GapExample( 175, 100, "Large Gap", 10, 20 );
}
}
addLayoutComponent(String,Component) layoutContainer(Container) minimumLayoutSize(Container) preferredLayoutSize(Container) removeLayoutComponent(Component) toString() A layout manager for a container that lays out grids
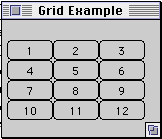
import java.awt.*;
class GridLayoutExample extends Frame {
public GridLayoutExample( int widthInPixels, int heightInPixels ) {
setTitle( "Grid Example" );
resize( widthInPixels, heightInPixels );
int numberOfRows = 4;
int numberOfColumns = 3;
setLayout( new GridLayout( numberOfRows,
numberOfColumns ) );
for ( int label = 1; label < 13; label++ )
add( new Button( String.valueOf( label ) ) );
show();
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
new GridLayoutExample( 175, 100 );
}
}
addLayoutComponent(String,Component) layoutContainer(Container) minimumLayoutSize(Container) preferredLayoutSize(Container) removeLayoutComponent(Component) toString()
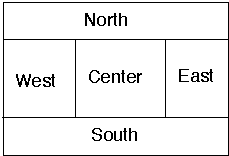
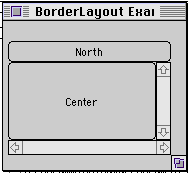
import java.awt.*;
class BorderLayoutExample extends Frame {
public BorderLayoutExample( int widthInPixels,
int heightInPixels ) {
setTitle( "BorderLayout Example" );
resize( widthInPixels, heightInPixels );
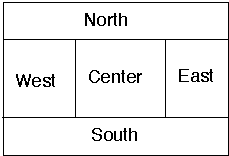
setLayout( new BorderLayout() );
add( "North", new Button( "North" ) );
add( "Center", new Button( "Center" ) );
add( "East", new Scrollbar( Scrollbar.VERTICAL ) );
add( "South", new Scrollbar( Scrollbar.HORIZONTAL ) );
show();
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
new BorderLayoutExample( 175, 100 );
}
}
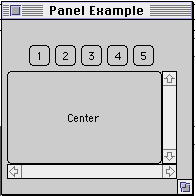
import java.awt.*;
class PanelExample extends Frame {
public PanelExample( int widthInPixels, int heightInPixels ) {
setTitle( "Panel Example" );
resize( widthInPixels, heightInPixels );
setLayout( new BorderLayout() );
Panel buttonDisplay = new Panel();
buttonDisplay.setLayout( new FlowLayout() );
for ( int label = 1; label < 6; label++ )
buttonDisplay.add( new Button( String.valueOf( label )) );
add( "North", buttonDisplay );
add( "Center", new Button( "Center" ) );
add( "East", new Scrollbar( Scrollbar.VERTICAL ) );
add( "South", new Scrollbar( Scrollbar.HORIZONTAL ) );
show();
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
new PanelExample( 175, 100 );
}
}
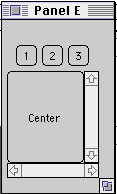
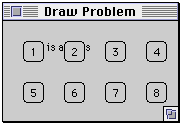
class DrawExample extends Frame {
public DrawExample( int width, int height ) {
setTitle( "Draw Problem" );
resize( width, height );
setLayout( new FlowLayout( FlowLayout.LEFT, 20, 20 ) );
for ( int label = 1; label < 10; label++ )
add( new Button( String.valueOf( label ) ) );
show();
}
public void paint( Graphics screen ) {
screen.drawString( "This is a mess", 20 , 30 );
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
new DrawExample( 175, 100 );
}
}
A canvas is a rectangular region which you can draw on.
class SimpleCanvas extends Canvas{
public void paint( Graphics drawOnMe ){
int startX = 0;
int startY = 0;
int endX = 30;
int endY = 30;
drawOnMe.drawLine( startX, startY, endX, endY );
int width = 5;
int height = 5;
drawOnMe.drawOval( endX, endY, width, height );
}
}
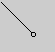
class CanvasExample extends Frame {
public CanvasExample( int widthInPixels, int heightInPixels ) {
setTitle( "Canvas Example" );
resize( widthInPixels, heightInPixels );
setLayout( new BorderLayout() );
Panel buttonDisplay = new Panel();
buttonDisplay.setLayout( new FlowLayout() );
for ( int label = 1; label < 6; label++ )
buttonDisplay.add( new Button( String.valueOf( label ) ) );
add( "North", buttonDisplay );
add( "Center", new SimpleCanvas() );
add( "East", new Scrollbar( Scrollbar.VERTICAL ) );
add( "South", new Scrollbar( Scrollbar.HORIZONTAL ) );
show();
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
new CanvasExample( 175, 150 );
}
}
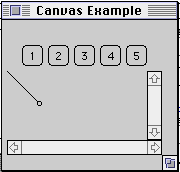
class CanvasProblem extends Frame {
public CanvasProblem( int widthInPixels, int heightInPixels ) {
setTitle( "Canvas Problem" );
resize( widthInPixels, heightInPixels );
setLayout( new BorderLayout() );
Panel buttonDisplay = new Panel();
buttonDisplay.setLayout( new FlowLayout() );
for ( int label = 1; label < 6; label++ )
buttonDisplay.add( new Button( String.valueOf( label ) ) );
add( "Center", buttonDisplay );
add( "North", new SimpleCanvas() );
add( "East", new Scrollbar( Scrollbar.VERTICAL ) );
add( "South", new Scrollbar( Scrollbar.HORIZONTAL ) );
show();
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
new CanvasProblem( 175, 150 );
}
}
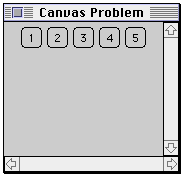
class SimpleCanvas extends Canvas{
Dimension preferredSize;
public SimpleCanvas( int width, int height ) {
preferredSize = new Dimension( width, height );
}
public void paint( Graphics drawOnMe ){
int startX = 0;
int startY = 0;
int endX = 30;
int endY = 30;
drawOnMe.drawLine( startX, startY, endX, endY );
int width = 5;
int height = 5;
drawOnMe.drawOval( endX, endY, width, height );
}
public Dimension preferredSize() {
return preferredSize;
}
public Dimension minimumSize() {
return new Dimension( 5, 5 );
}
}
class CanvasProblem extends Frame {
public CanvasProblem( int widthInPixels, int heightInPixels ) {
setTitle( "Canvas Fixed" );
resize( widthInPixels, heightInPixels );
setLayout( new BorderLayout() );
Panel buttonDisplay = new Panel();
buttonDisplay.setLayout( new FlowLayout() );
for ( int label = 1; label < 6; label++ )
buttonDisplay.add( new Button( String.valueOf( label ) ) );
add( "Center", buttonDisplay );
add( "North", new SimpleCanvas( 20, 30 ) );
add( "East", new Scrollbar( Scrollbar.VERTICAL ) );
add( "South", new Scrollbar( Scrollbar.HORIZONTAL ) );
show();
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
new CanvasProblem( 175, 150 );
}
}
addLayoutComponent(String,Component) first(Container) last(Container) layoutContainer(Container) minimumLayoutSize(Container) next(Container) preferredLayoutSize(Container) previous(Container) removeLayoutComponent(Component) show(Container,String) toString()
import java.awt.*;
class CardLayoutExample extends Frame {
CardLayout threeCards;
Panel deck;
public CardLayoutExample( int widthInPixels, int heightInPixels )
{
setTitle( "CardLayoutExample Example" );
resize( widthInPixels, heightInPixels );
setLayout( new BorderLayout() );
threeCards = new CardLayout();
deck = new Panel();
deck.setLayout( threeCards );
deck.add( "Ace", new Button( "Ace" ) );
deck.add( "King", new Button( "King" ) );
deck.add( "Queen", new Button( "Queen" ) );
add( "Center", deck );
add( "North", new Button( "Next" ) );
show();
}
public boolean action( Event processNow, Object buttonPressed ) {
if ( buttonPressed.equals( "Next" ) )
threeCards.next( deck );
else return super.action( processNow, buttonPressed );
return true;
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
new CardLayoutExample(200, 200);
}
}
| anchor | HORIZONTAL | REMAINDER | |
| BOTH | insets | SOUTH | |
| CENTER | ipadx | SOUTHEAST | |
| EAST | ipady | SOUTHWEST | |
| fill | NONE | VERTICAL | |
| gridheight | NORTH | weightx | |
| gridwidth | NORTHEAST | weighty | |
| gridx | NORTHWEST | WEST | |
| gridy | RELATIVE |
addLayoutComponent(String,Component) AdjustForGravity(GridBagConstraints,Rectangle) ArrangeGrid(Container) getConstraints(Component) getLayoutDimensions() GetLayoutInfo(Container,int) getLayoutOrigin() getLayoutWeights() GetMinSize(Container,GridBagLayoutInfo) layoutContainer(Container) location(int,int) lookupConstraints(Component) minimumLayoutSize(Container) preferredLayoutSize(Container) removeLayoutComponent(Component) setConstraints(Component,GridBagConstraints) toString()