
Spring Semester, 2005
Introduction
© 2005, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney
San Diego State University -- This page last updated 24-Jan-05

|
Client-Server Programming
Spring Semester, 2005 Introduction |
|
|---|---|---|
|
© 2005, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney San Diego State University -- This page last updated 24-Jan-05 |
CS 580 Client-Server Programming Spring Semester, 2005 Doc 1 Introduction
What Client-Server Requires of a Programmer
Naming Convention for Classes, Variables & Methods
Copyright ©, All rights reserved. 2004 SDSU & Roger Whitney, 5500 Campanile Drive, San Diego, CA 92182-7700 USA. OpenContent ( http://www.opencontent.org/opl.shtml) license defines the copyright on this document
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 2 |
Code Complete by Steve McConnell
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 3 |
Introduction
Testing
Source Version Control
Network Basics
GUI
Client Development Issues
Concurrency
Server Types & Structure
Client-Server Protocols
Logging
Databases
Security
Web based Applications
Web Services
Advanced topics
This outline will be changed during the semester.
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 4 |
Common design issues & solutions for building a server
Issues in designing a client-server network protocol
Handling Concurrency
Accessing databases
Programming issues dealing with working on client-server code
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 5 |
Java
Smalltalk – VisualWorks 7.3
C#
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 6 |
Basic syntax of the language
Core API
Language culture - Ways of doing things in each language
Object-oriented programming
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 7 |
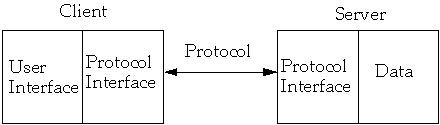
Client
Server
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 8 |
An advanced (or beginning) Networking course

How to use a client builder application/system
Skills & knowledge required to build client-server applications
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 9 |
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 10 |
Capitalize the first character of each word
SomeClassName
Capitalize the first character of each word except the first word
someVariableName
|
Item |
Java |
Smalltalk |
C# |
|
Class |
PascalCase |
PascalCase |
PascalCase |
|
Method |
camelCase |
camelCase |
PascalCase |
|
Field |
camelCase |
camelCase |
CamelCase |
|
Parameter |
camelCase |
camelCase |
camelCase |
|
Local Variable |
camelCase |
camelCase |
camelCase |
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 11 |
"Finding good names is the hardest part of OO Programming"
"Names should fully and accurately describe the entity the variable represents"
What role does the variable play in the program?
|
Data Structure |
Role, function |
|
InputRec |
EmployeeData |
|
BitFlag |
PrinterReady |
|
TrainVelocity |
Velt, V, X, Train |
|
CurrentDate |
CD, Current, C, X, Date |
|
LinesPerPage |
LPP, Lines, L, X |
Names should be as short as possible and still convey meaning to the reader
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 12 |
"Comments are easier to write poorly than well, and comments can be more damaging than helpful"
for i := 1 to Num do MeetsCriteria[ i ] := True; for i := 1 to Num / 2 do begin j := i + i; while ( j <= Num ) do begin MeetsCriteria[ j ] := False; j := j + i; end; for i := 1 to Mun do if MeetsCriteria[ i ] then writeln( i, ' meets criteria ' );
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 13 |
for PrimeCandidate:= 1 to Num do
IsPrime[ PrimeCandidate] := True;
for Factor:= 1 to Num / 2 do begin
FactorableNumber := Factor + Factor ;
while ( FactorableNumber <= Num ) do begin
IsPrime[ FactorableNumber ] := False;
FactorableNumber := FactorableNumber + Factor ;
end;
end;
for PrimeCandidate:= 1 to Num do
if IsPrime[ PrimeCandidate] then
writeln( PrimeCandidate, ' is Prime ' );
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 14 |
Write comments at the level of the code's intent
Comment the why rather than the how
Make every comment count
Document surprises
Avoid abbreviations
/* if allocation flag is zero */ if ( AllocFlag == 0 ) ...
/* if allocating a new member */ if ( AllocFlag == 0 ) ...
if ( AllocFlag == NEW_MEMBER ) ...
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 15 |
{ check each character in "InputStr" until a
dollar sign is found or all characters have
been checked }
Done := false;
MaxPos := Length( InputStr );
i := 1;
while ( (not Done) and (i <= MaxLen) ) begin
if ( InputStr[ i ] = '$' ) then
Done := True
else
i := i + 1
end;
{ find the command-word terminator }
Done := false;
MaxPos := Length( InputStr );
i := 1;
while ( (not Done) and (i <= MaxPos ) ) begin
if ( InputStr[ i ] = '$' ) then
Done := True
else
i := i + 1
end;
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 16 |
{ find the command-word terminator }
FoundTheEnd := false;
MaxCommandLength := Length( InputStr );
Index := 1;
while ((not FoundTheEnd) and
(Index <= MaxCommandLength)) begin
if ( InputStr[ Index ] = '$' ) then
FoundTheEnd := True;
else
Index := Index + 1;
end;
| CS 580 Spring 05 | Doc 1, Introduction Slide # 17 |
Comment the units of numeric data
Comment the range of allowable numeric values
Comment coded meanings
var
CursorX: 1..MaxCols; { horizontal screen position of cursor }
CursorY: 1..MaxRows; { vertical position of cursor on screen }
AntennaLength: Real; { length of antenna in meters: >= 2 }
SignalStrength: Integer; { strength of signal in kilowatts: >= 1 }
CharCode: 0..255; { ASCII character code }
CharAttib: Integer; { 0=Plain; 1=Italic; 2=Bold }
CharSize: 4..127; { size of character in points }
Comment limitations on input data
Document flags to the bit level
Copyright ©, All rights reserved.
2005 SDSU & Roger Whitney, 5500 Campanile Drive, San Diego, CA 92182-7700 USA.
OpenContent license defines the copyright on this document.