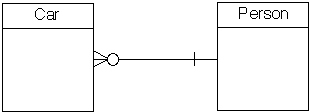|
CS 580 Client-Server
Spring Semester, 2004
SQL & Normalization
|
|
|
|
Previous
Lecture Notes Index
Next
© 2004, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney
San Diego State University -- This page last updated 05-Feb-04
|
|
References
Oracle
Design, Ensor & Stevenson, O'Reilly & Associates, Inc., 1997
MySQL
On-line Manual
http://www.mysql.com/doc/en/Reference.html
PostgreSQL
Commands
http://www.postgresql.org/idocs/index.php?sql-commands.html
Some
Data Modeling
Terms
Entity
- A
distinct class of things about which something is known
Entity
Occurrence
- Particular
instance of an entity class
- In
a database entity occurrences are records in a table
Attribute
- An
abstraction belonging to or characteristic of an entity
Primary
Key (unique identifier)
- An
attribute (or set of attributes) that uniquely define an entity
Relationship
- An
abstraction belonging to or characteristic of two entities or parts together
Relational
databases do not support pointers to entities
Foreign
Key
- A
unique identifier in a record representing another record
Entity
Relationship Diagram (ERD)
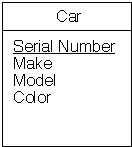
Entity
(car) with:
- Attributes
(Color, make, model, serial number)
- Primary
key (serial number)
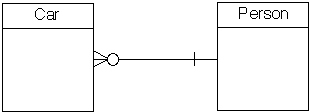
Relationship
between Car and Person entities
- Car
must have one and only one owner
- Person
may own zero, one or more cars
- Person
can own many cars
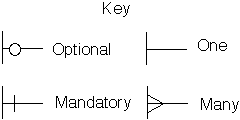
An
Example
Primary
Key
A
primary key is one that uniquely identifies a row in a table
A
Silly Table
name
|
faculty_id
|
Whitney
|
1
|
Beck
|
2
|
Anantha
|
3
|
PostgreSQL
Version
CREATE TABLE faculty (
name CHAR(20) NOT NULL,
faculty_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY
);
MySQL
Version
CREATE TABLE faculty (
name CHAR(20) NOT NULL,
faculty_id INTEGER AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY
);
Indices
Indices
make accessing faster
Primary
keys automatically have an index
The
CREATE INDEX command creates indices
CREATE INDEX faculty_name_key on faculty (name);
Adding
Values
INSERT INTO faculty ( name) VALUES ('Whitney');
INSERT INTO faculty ( name) VALUES ('Beck');
INSERT INTO faculty ( name) VALUES ('Anantha');
INSERT INTO faculty ( name) VALUES ('Vinge');
select * from faculty;
Result
name | faculty_id
----------------------+-------------
Whitney | 1
Beck | 2
Anantha | 3
Vinge | 4
(4 rows)
Note
PostgreSQL allows one to drop the list of column names:
INSERT INTO faculty VALUES ('Vinge');
A
Second Table
PostgreSQL
CREATE TABLE office_hours (
start_time TIME NOT NULL,
end_time TIME NOT NULL,
day CHAR(3) NOT NULL,
faculty_id INTEGER REFERENCES faculty,
office_hour_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY
);
MySQL
CREATE TABLE office_hours (
start_time TIME NOT NULL,
end_time TIME NOT NULL,
day CHAR(3) NOT NULL,
faculty_id INTEGER REFERENCES faculty,
office_hour_id INTEGER AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY
);
REFERENCES
faculty insures that only valid references are made
start_time
|
end_time
|
day
|
faculty_id
|
office_hour_id
|
10:00
|
11:00
|
Wed
|
1
|
1
|
8:00
|
12:00
|
Mon
|
2
|
2
|
17:00
|
18:30
|
Tue
|
1
|
3
|
9:00
|
10:30
|
Tue
|
3
|
4
|
9:00
|
10:30
|
Thu
|
3
|
5
|
15:00
|
16:00
|
Fri
|
1
|
6
|
Office_Hours
adding
Simple
Insert
INSERT
INTO office_hours ( start_time, end_time, day, faculty_id )
VALUES ( '10:00:00', '11:00:00' , 'Wed', 1 );
The
problem is that we need to know the id for the faculty
Using
Select
INSERT INTO
office_hours (start_time, end_time, day, faculty_id )
SELECT
'8:00:00' AS start_time,
'12:00:00' AS end_time,
'Mon' AS day,
faculty_id AS faculty_id
FROM
faculty
WHERE
name = 'Beck';
Getting
Office Hours
SELECT
name, start_time, end_time, day
FROM
office_hours, faculty
WHERE
faculty.faculty_id = office_hours.faculty_id;
name
|
start_time
|
end_time
|
day
|
Whitney
|
10:00:00
|
11:00:00
|
Wed
|
Beck
|
08:00:00
|
12:00:00
|
Mon
|
Whitney
|
17:00:00
|
18:30:00
|
Tue
|
Whitney
|
15:00:00
|
16:00:00
|
Fri
|
Anantha
|
09:00:00
|
10:30:00
|
Tue
|
Anantha
|
09:00:00
|
10:30:00
|
Thu
|
Some
Formatting
PostgreSQL
only
SELECT
name AS Instructor,
TEXT(start_time) || ' to ' || TEXT(end_time) AS Time,
day AS Day
FROM
office_hours, faculty
WHERE
faculty.faculty_id = office_hours.faculty_id
ORDER BY
Name;
Instructor
|
Time
|
Day
|
Anantha
|
09:00:00
to 10:30:00
|
Tue
|
Anantha
|
09:00:00
to 10:30:00
|
Thu
|
Beck
|
08:00:00
to 12:00:00
|
Mon
|
Whitney
|
10:00:00
to 11:00:00
|
Wed
|
Whitney
|
17:00:00
to 18:30:00
|
Tue
|
Whitney
|
15:00:00
to 16:00:00
|
Fri
|
Some
Selection
SELECT
name, start_time, end_time, day
FROM
office_hours, faculty
WHERE
faculty.faculty_id = office_hours.faculty_id
AND
start_time > '09:00:00'
AND
end_time < '16:30:00'
ORDER BY
Name;
name
|
start_time
|
end_time
|
day
|
Whitney
|
10:00:00
|
11:00:00
|
Wed
|
Whitney
|
15:00:00
|
16:00:00
|
Fri
|
Normalization
Defined
by Dr. E. F. Codd in 1970
Normal
forms
- Reduce
redundant data and inconsistencies
First
Normal Form (1NF)
An
entity is in the first normal form when all its attributes are single valued
Example
- Office Hours
Name
|
OfficeHour1
|
OfficeHour2
|
OfficeHour3
|
Whitney
|
10:00-11:00
W
|
17:00-18:30
Tu
|
15:00-16:00
Fri
|
Beck
|
8:00-12:00
M
|
|
|
Anantha
|
9:00-10:30
Tu
|
9:00-10:30
Thu
|
|
What
if someone has more than 3 office hours?
Wasted
space for those that have fewer office hours
Not
is 1NF since office hours are repeated
In
1NF Form
Faculty
name
|
faculty_id
|
Whitney
|
1
|
Beck
|
2
|
Anantha
|
3
|
Office
Hours
start_time
|
end_time
|
day
|
faculty_id
|
office_hour_id
|
10:00
|
11:00
|
Wed
|
1
|
1
|
8:00
|
12:00
|
Mon
|
2
|
2
|
17:00
|
18:30
|
Tue
|
1
|
3
|
9:00
|
10:30
|
Tue
|
3
|
4
|
9:00
|
10:30
|
Thu
|
3
|
5
|
15:00
|
16:00
|
Fri
|
1
|
6
|
Second
Normal Form (2NF)
An
entity is in the second normal form if:
- It
is in 1NF and
- All
non-key attributes must be fully dependent on the entire primary key
Example
1- CDs
Put
your collection of CD in a database
cd_title
|
artist
|
music_type
|
cd_id
|
Songs
from the Trilogy
|
Glass
|
Modern
Classical
|
1
|
I
Stoten
|
Falu
Spelmanslag
|
Swedish
|
2
|
Photographer
|
Glass
|
Modern
Classical
|
3
|
etc.
|
|
|
|
Table
is not in 2NF since different CDs
- Can
have the same artists
- Can
have same music type
Example
2- Course Schedule
Name
|
Time
|
Days
|
Term
|
Schedule
Number
|
CS635
|
1700-1815
|
MW
|
Spring01
|
09461
|
CS651
|
1700-1815
|
MW
|
Spring01
|
09472
|
CS672
|
1700-1815
|
MW
|
Spring01
|
09483
|
CS683
|
1830-1945
|
MW
|
Spring01
|
09494
|
CS696
|
1530-1645
|
MW
|
Spring01
|
09505
|
CS696
|
1830-1945
|
MW
|
Spring01
|
09516
|
CS696
|
1530-1645
|
TTh
|
Spring01
|
09520
|
At
SDSU the schedule number uniquely identifies a course in a semester
So
the term and schedule number uniquely identifies a course at SDSU
We
can use term and schedule as the primary key
The
table is in 1NF but not 2NF
Name,
Time and Days are not fully dependent on the primary key
Schedule
course_id
|
time_id
|
term_id
|
schedule_number
|
1
|
1
|
2
|
09461
|
2
|
1
|
2
|
09472
|
3
|
1
|
2
|
09483
|
4
|
2
|
2
|
09494
|
Courses
course
|
title
|
name_id
|
CS635
|
Adv
Obj Orient Dsgn Prog
|
1
|
CS651
|
Adv
Multimedia Systems
|
2
|
CS672
|
Micro
Computer Software
|
3
|
CS683
|
Emerging
Technologies
|
4
|
CS696
|
Intell
Systems & Control
|
5
|
CS696
|
Writing
Device Drivers
|
6
|
CS696
|
Sem:
Computer Security
|
7
|
Time
start_time
|
end_time
|
days
|
time_id
|
17:00:00
|
18:15:00
|
MW
|
1
|
18:30:00
|
19:45:00
|
MW
|
2
|
15:30:00
|
16:45:00
|
MW
|
3
|
15:30:00
|
16:45:00
|
TTh
|
4
|
Etc.
|
|
|
|
Term
semester
|
year
|
term_id
|
Fall
|
2000
|
1
|
Spring
|
2001
|
2
|
Comments
about Previous Slide
The
schedule table is now in 2NF
What
about the other tables?
If
not how would you fix them?
Can
you find a better way to decompose the original table?
Third
Normal Form (3NF)
An
entity is in third normal form if
- It
is in 2NF and
- All
non-key attributes must only be dependent on the primary key
Customer
Name
|
Address
|
City
|
State
Name
|
State
abbreviation
|
zip
|
id
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
State
abbreviation depends on State Name
Table
is not in 3NF
Other
Normal Forms
- Boyce-Codd
normal form (BCNF)
- Fourth
normal form (4NF)
- Fifth
normal form (5NF)
These
are beyond the scope of this course
See
your local database course/textbook
Copyright ©, All rights reserved.
2004 SDSU & Roger Whitney, 5500 Campanile Drive, San Diego, CA 92182-7700 USA.
OpenContent license defines the copyright on this document.
Previous
 visitors since 05-Feb-04
Next
visitors since 05-Feb-04
Next