
Fall Semester, 2004
CSS
© 2004, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney
San Diego State University -- This page last updated 06-Sep-04

|
Emerging Technology
Fall Semester, 2004 CSS |
|
|---|---|---|
|
© 2004, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney San Diego State University -- This page last updated 06-Sep-04 |
CS 683 Emerging Technologies Fall Semester, 2004 Doc 2 CSS
Linking to an External Style Sheet
Linking Styles to Html – Selectors
Copyright ©, All rights reserved. 2004 SDSU & Roger Whitney, 5500 Campanile Drive, San Diego, CA 92182-7700 USA. OpenContent ( http://www.opencontent.org/opl.shtml) license defines the copyright on this document.
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 2 |
CSS Pocket Reference, 2 nd Ed., Eric Meyer, O’Reilly, 2004
Web Design Group’s Guide to Style Sheets, http://www.htmlhelp.com/reference/css/
Cascading Style Sheets, level 2 revision 1 CSS 2.1 Specification http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS21/
http://www.randsinrepose.com/archives/2004/05/04/your_redesign_toolbox.html
http://www.csszengarden.com/ css Zen Garden –
This site is amazing. With the same html page, a number of completely different pages are displayed. You have to see this site to see how different one can vary the display of one page.
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 3 |
A language to describe the layout of html and xml pages
<p style="color: red; background: blue;margin: 0.5em;"> This is an example of inline css. </p> <p style="color: red; font-size: xx-large;text-align: center; "> Use Inline CSS sparingly! </p>
This is an example of inline css.
Use Inline CSS sparingly!
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 4 |
1960s – Standard General Markup Language (SGML)
Large companies (like General Motors, IBM) and the US government worked to create SGML to define document structure. Computer then could be used to print the document. Since SGML defined just the structure and not how to display the document, a document could be layed out in many different ways. Also the document could be searched and parts of the document used in other documents.
1990s – HTML
The creators of HTML really missed the point of SGML. HTML was simple and worked, but scaled poorly. It contains tags and attributes that describe layout, making it hard to maintain a number of pages and modify the layout over time and on differing types of devices.
<center>Center the text</center>
<td width=”105”>A Wide table data cell</td>
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 5 |
Use CSS for layout Use html (xhtml) to define the structure of the page
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 6 |
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 7 |
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.1//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml11/DTD/xhtml11.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=iso-8859-1" />
<title>Sample</title>
<meta name="generator" content="BBEdit 7.1.4" />
<link rel="Stylesheet" href="simple.css" type="text/css" media="all" />
</head>
<body>
<p>A Smalltalk example </p>
<p class="code">1000 factorial printString size</p>
</body>
</html>
p.code
{
margin: 0 .5in 0 .5in;
padding: 5px;
border-style: solid;
border-width: 1px;
border-color: #CCCCCC;
background-color: #F4F4F4;
}
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 8 |
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.1//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml11/DTD/xhtml11.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=iso-8859-1" />
<title>Sample</title>
<meta name="generator" content="BBEdit 7.1.4" />
<link rel="Stylesheet" href="simple.css" type="text/css" media="screen" />
<link rel="Stylesheet" href="small.css" type="text/css" media="handheld" />
<link rel="Stylesheet" href="print.css" type="text/css" media="print" />
</head>
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 9 |
all
braille
Braille tactile feedback devices.
embossed
Intended for paged braille printers.
handheld
Intended for handheld devices
Intended for paged material and for documents viewed on screen in print preview mode.
projection
Intended for projected presentations, for example projectors.
screen
Intended primarily for color computer screens.
speech
Intended for speech synthesizers
tty
Intended for media using a fixed-pitch character grid
tv
Intended for television-type devices
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 10 |
<link rel="StyleSheet" href="basics.css" title="Contemporary" /> <link rel="StyleSheet" href="tables.css" title="Contemporary" /> <link rel="StyleSheet" href="forms.css" title="Contemporary" />
Since all three links have the same title they form a single style sheet
If basics.css contains:
p.code { margin: 0 .5in 0 .5in; }
and tables.css contains:
p.code { margin: 0 2in 0 .2in; }
Then the later is used as tables.css is linked after basics.css
There are a number of ways to link multiple styles sheets to a document. When style definitions clash the later one is used.
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 11 |
<link rel="StyleSheet" href="basics.css" />
rel=”StyleSheet” indicates the style is persistent
persistent style is one that is used when style sheets are enabled
<link rel="alternate stylesheet" href="basics.css" />
rel=”alternate stylesheet” indicates an alternative style
Currently most browsers do not provide the ability to select and alternative style sheet
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 12 |
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.1//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml11/DTD/xhtml11.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=iso-8859-1" />
<title>Sample</title>
<meta name="generator" content="BBEdit 7.1.4" />
<style type="text/css" media="all">
<!--
p.code
{
margin: 0 .5in 0 .5in;
padding: 5px;
border-style: solid;
border-width: 1px;
border-color: #CCCCCC;
background-color: #F4F4F4;
}
-->
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>A Smalltalk example </p>
<p class="code">1000 factorial printString size</p>
</body>
</html>
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 13 |
Some early browsers do not know about style sheets
They will display the style sheet
<style type="text/css" media="all">
<!--
p.code {margin: 0 .5in 0 .5in; }
-->
</style>
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 14 |
<style type="text/css" media="screen, projection">
<!--
@import url(http://www.htmlhelp.com/style.css);
@import url(/stylesheets/punk.css);
dt { background: yellow; color: black }
-->
</style>
import statements must be at the top of a style tag External style sheets (linked or imported) can also import other style sheets
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 15 |
A style or rule has a selector and one or more declarations
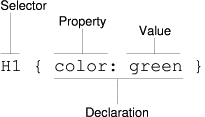
Image from http://www.w3.org/Style/LieBos2e/enter/
See http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS21/selector.html#q1 for a table of all types of selectors
See http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS21/selector.html for details of each selector type
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 16 |
h1
{
font-style: normal;
font-weight: bolder;
text-align: center;
font-size: medium;
}
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 17 |
h1
{
font-style: normal;
text-align: center;
}
h2
{
font-style: normal;
text-align: center;
}
The above two rules can be combined into one rule
h1, h2
{
font-style: normal;
text-align: center;
}
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 18 |
h1 { color: red }
em { color: red }
h1 em { color: blue }
h1 em will match any em tag that is nested in a h1 tag
<H1>This <SPAN class="myclass">headline is <EM>very</EM> important</SPAN></H1>
You can nest selecters as deep as you need
h1 td ul il a { color: green }
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 19 |
h1 > em { color: blue }
h1 > em will match any em tag that is directly inside a h1 tag It does not match the em tag below
<H1>This <SPAN class="myclass">headline is <EM>very</EM> important</SPAN></H1>
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 20 |
* matches any tag
* { color: green }
h1 > * { color: blue
The later makes all child tags of h1 blue
table + p { color: green }
Matches a <p> that follows a table The rule matches the following <p> pure text between table and p are ignored
<table border="1"><tr><td>A Cell</td></tr> </table> foo <p>bar</p>
There are no matches below
<table border="1"><tr><td>A Cell</td></tr> </table> <div>foo</div> <p>bar</p>
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 21 |
<div name="sam">1</div> <p name="sam" >2</p> <p>3</p> <a href="index.html" name="pete">4</a> <p name="sam roger pete" >5</p>
[name] { color: lightblue}
Results in
2
3
45
a[name] { color: lightblue}
Results in
2
3
45
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 22 |
[name=pete] {color: lightblue}
Results in
2
3
45
[name~=pete] {color: lightblue; }
Results in
2
3
45
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 23 |
[att]
Match when the element sets the "att" attribute, whatever the value of the attribute.
[att=val]
Match when the element's "att" attribute value is exactly "val".
[att~=val]
Match when the element's "att" attribute value is a space-separated list of "words", one of which is exactly "val".
[att|=val]
Match when the element's "att" attribute value is a hyphen-separated list of "words", beginning with "val". The match always starts at the beginning of the attribute value.
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 24 |
class is a special attribute of tags
<div class="sam">1</div> <p class="sam" >2</p> <p>3</p> <a class="pete">4</a> <p name="roger sam pete" >5</p>
.sam { color: lightblue }
Results in
2
3
45
p.sam { color: lightblue }
Results in
2
3
45
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 25 |
Two id attributes cannot have the same value in a single document
Browser vary on how they enforce this rule
#sam { color: lightblue }
matches both
<p id="sam" >2</p> <a id="pete">4</a>
However
p#sam { color: lightblue }
matches
<p id="sam" >2</p>
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 26 |
Div is a block-level element used to group other elements Block-level elements usually start on a new line
<div class="note">
<h1>Divisions</h1>
<p>
The DIV element is defined in HTML 3.2, but
only the ALIGN attribute is permitted in HTML 3.2.
HTML 4.0 adds the CLASS, STYLE, and ID attributes,
among others.
</p>
<p>
Since DIV may contain other block-level
containers, it is useful for marking large sections
of a document, such as this note.
</p>
<p>
The closing tag is required.
</p>
</div>
div.note { color: lightblue }
Matches all the elements above
When you match an element you match all the elements inside it
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 27 |
Span is an inline element used to use style that cannot be attached to regular html elements Inline elements usually do not begin on a new line
<p> <span class="firstwords">The first few words</span> of a paragraph could be in small-caps. Style may also be inlined, such as to change the style of a word like <span style="font-family: Arial"> Arial</span>. </p>
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 28 |
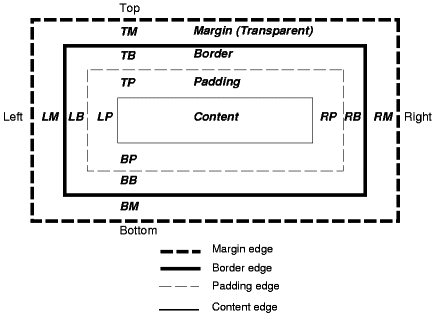
Image from http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS21/box.html
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 29 |
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.0//EN">
<HTML> <HEAD>
<TITLE>Examples of margins, padding, and borders</TITLE>
<STYLE type="text/css">
UL {
background: yellow;
margin: 12px 12px 12px 12px;
padding: 3px 3px 3px 3px; }
LI {
color: white; /* text color is white */
background: blue; /* Content, padding will be blue */
margin: 12px 12px 12px 12px;
padding: 12px 0px 12px 12px; /* Note 0px padding right */
list-style: none /* no glyphs before a list item */
}
LI.withborder {
border-style: dashed;
border-width: medium; /* sets border width on all sides */
border-color: lime; }
</STYLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<UL>
<LI>First element of list
<LI class="withborder">Second element of list is
a bit longer to illustrate wrapping.
</UL>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Example from http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS21/box.html
| CS 683 Fall 04 | Doc 2, CSS Slide # 30 |
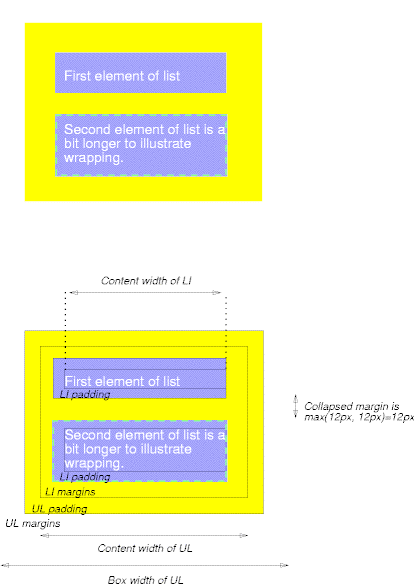
Image from http://www.w3.org/TR/CSS21/box.html
Copyright ©, All rights reserved.
2004 SDSU & Roger Whitney, 5500 Campanile Drive, San Diego, CA 92182-7700 USA.
OpenContent license defines the copyright on this document.