
Fall Semester, 2000
Servers & States
© 2000, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney
San Diego State University -- This page last updated 01-Nov-00

|
CS 580 Client-Server Programming Fall Semester, 2000 Servers & States |
|
|---|---|---|
|
© 2000, All Rights Reserved, SDSU & Roger Whitney San Diego State University -- This page last updated 01-Nov-00 |
Servers & States
Common operations of servers
Some Context Assume we are writing a server to handle Airline reservation system
Assume there are three possible commands from client to server:
interface ServerEngine
{
public ServerEngine newInstance(ProgramProperties settings);
public ServerEngine cleanInstance( );
public void processRequest(InputStream in, OutputStream out,
InetAddress clientAddress) throws IOException;
}
We
have a class ProtocolParser, which will parse the protocol
Using If statements to Handle a Request
class AirlineServer implements ServerEngine { public void processRequest(InputStream in, OutputStream out, InetAddress clientAddress) throws IOException { ProtocolParser requestData = new ProtocolParser( in ); String request = requestData.getCommand(); if (request.equals( "getCities" )) call get cities code else if (request.equals( "getLunchMenu" )) call get lunch code else if (request.equals( "getManifest" )) call get manifest code else //illegal request deal with illegal request etc. } }
For small number of commands if/switch statements work well
Complex Case - States
An Example
SPOP
Example protocol: Simple Post Office Protocol (SPOP)
Commands have the same functionality as POP but are limited to the following:
USER <username>
PASS <password>
LIST
RETR <message number>
QUIT
SPOP features
The authentication consists of two commands that have to come in sequence:
USER
PASS
The other commands (except for QUIT) cannot be executed before the user has been authenticated.
What does this mean for the client and server?
Parsing
Simple approach:
start: get command if command is "USER" then username = argument get command if command is "PASS" then password = argument if valid(username,password) then while true get command if command is "LIST" then performLIST elsif command is "RETR" then performRETR(argument) elsif command is "QUIT" then return end if end while end if end if end if
Simple Parsing Problems
Major problems with this algorithm:
Finite Automata - State Machines
A better way of looking at all of this is using a picture.
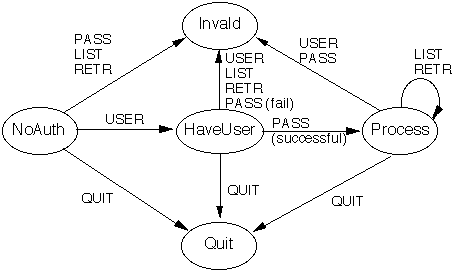
Naming the states
We will use the following names for the states:
|
0 |
NoAuth
|
|
1 |
HaveUser
|
|
2 |
Process
|
|
3 |
Invalid
|
|
4 |
Quit |
Implementing a State Machine: switch
int state = 0; while (true) { command = next command; switch (state) { case 0: if (command.equals("USER")) { username = argument; state = 1; } else if (command.equals("QUIT")) state = 4; else error("Unknown: " + command); break; case 1: if (command.equals("PASS")) { if (valid(username, argument)) state = 2; else { error("Unauthorized"); state = 3; } } else error("Unknown: " + command); break; ...
Switch Method Analysis
Major problems with this algorithm:
Implementing a State Machine: Table
|
Commands |
States |
||||
|
NoAuth |
HaveUser |
Process |
Invalid |
Quit |
|
|
USER |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PASS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
LIST |
|
|
|
|
|
|
RETR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
QUIT |
|
|
|
|
|
The State Table
|
Commands |
States |
||||
|
NoAuth |
HaveUser |
Process |
Invalid |
Quit |
|
|
USER |
actionUser |
actionNull |
actionNull |
|
|
|
HaveUser |
Invalid |
Invalid |
Quit |
Quit |
|
|
Invalid |
Invalid |
Invalid |
Quit |
Quit |
|
|
PASS |
actionNull |
actionPass |
actionNull |
|
|
|
Invalid |
Process |
Invalid |
Quit |
Quit |
|
|
Invalid |
Invalid |
Invalid |
Quit |
Quit |
|
|
LIST |
actionNull |
actionNull |
actionList |
|
|
|
Invalid |
Invalid |
Process |
Quit |
Quit |
|
|
Invalid |
Invalid |
Invalid? |
Quit |
Quit |
|
|
RETR |
actionNull |
actionNull |
actionRetr |
|
|
|
Invalid |
Invalid |
Process |
Quit |
Quit |
|
|
Invalid |
Invalid |
Invalid? |
Quit |
Quit |
|
|
QUIT |
actionQuit |
actionQuit |
actionQuit |
|
|
|
Quit |
Quit |
Quit |
Quit |
Quit |
|
|
Quit |
Quit |
Quit |
Quit |
Quit |
|
|
Function
to process request
|
|
Next
State on success
|
|
Next
State on failure
|
Function Pointers in C/C++
void quickSort( int* array, int LowBound, int HighBound) { // source code to sort array from LowBound to HighBound // using quicksort has been removed to save room on page } void mergeSort(int* array, int LowBound, int HighBound) { // same here} void insertionSort(int* array, int LowBound, int HighBound) { // ditto } void main() { void (*sort) (int*, int, int); int size; int data[100]; // pretend data and Size are initialized if (size < 25) sort = insertionSort; else if (size > 100) sort = quickSort; else sort = mergeSort; sort(data, 0, 99); }
C/C++ Function Pointers & Airline Example
typedef struct { char *command; int (*function)( char*); } vector; vector commandTable[] = { {"Cities", getCitiesList}, {"LunchMenu", getLunchMenu}, {"Manifest", getFlightManifest} }; void executeCommand( char* inputLine, vector commandTable) { char* command = getCommand( inputLine ); for ( int k = 0, k < TABLESIZE; k++ ) if ( strcmp( command, commandTable[k].command ) == 0 ) commandTable[k].function( inputLine ); }
Notes:
SPOP State table: C/C++
In C/C++ we can define the following:
struct { int currentState; char *command; int stateIfSucceed; int stateIfFailed; int (*action)(char **); } actionTable[] = { {0, "USER", 1, 3, actionUser}, {0, "QUIT", 4, 4, actionQuit}, {1, "PASS", 2, 3, actionPass}, {1, "QUIT", 4, 4, actionQuit}, {2, "LIST", 2, 2, actionList}, {2, "RETR", 2, 2, actionList}, {2, "QUIT", 4, 4, actionList}, {0, 0, 0, 0, 0} };
Advantages:
Function Pointers in Java
Use Reflection
Class.getMethod maps strings to methods
public Method getMethod(String name,Class parameterTypes[]) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException
Returns a Method object that reflects the specified public member method of the class or interface represented by this Class object. The name parameter is a String specifying the simple name the desired method, and the parameterTypes parameter is an array of Class objects that identify the method's formal parameter types, in declared order.
The method to reflect is located by searching all the member methods of the class or interface represented by this Class object for a public method with the specified name and exactly the same formal parameter types.
Throws: NoSuchMethodException if a matching method is not found. Throws: SecurityException if access to the information is denied.
Simple Class for Example
class Example { public void getLunch() { System.out.println( "Lunch Time!"); } public void getLunch( String day) { System.out.println( "Lunch Time for " + day); } public void eatOut( String where) { System.out.println( "MacDonalds? "); } public void eatOut( int where) { System.out.println( "PizzaHut? " + where ); } }
Using Class.getMethodSimple Example
import java.lang.reflect.Method; class Test { public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception { Example a = new Example(); Class[] stringType = { Class.forName( "java.lang.String" ) }; Object[] stringParameter = { "Monday" }; Method tryMe; tryMe = a.getClass().getMethod( "getLunch", stringType ); tryMe.invoke( a, stringParameter ); } }
Output Lunch Time for Monday
Using Class.getMethod - Some Details
import java.lang.reflect.Method; class Test { public static void main( String args[] ) throws Exception { Example a = new Example(); Class[] stringType = { Class.forName( "java.lang.String" ) }; Class[] intType = { java.lang.Integer.TYPE }; Class[] noType = { }; Object[] stringParameter = { "Monday" }; Object[] intParameter = { new Integer(6) }; Object[] noParameter = { }; Method tryMe; tryMe = a.getClass().getMethod( "getLunch", stringType ); tryMe.invoke( a, stringParameter ); tryMe = a.getClass().getMethod( "getLunch", noType); tryMe.invoke( a, noParameter ); tryMe = a.getClass().getMethod( "eatOut", intType ); tryMe.invoke( a, intParameter ); } }Output Lunch Time for Monday
Lunch Time
PizzaHut? 6
Airline Example
class AirlineServer implements ServerEngine { public String getCitiesList( ) { blah } public String getLunchMenu( ) { blah } public String getFlightManifest( String usedHere ) { blah } public String invoke( String methodName, String argument ) { Class[] argType = { }; Object[] parameter = { }; if ( argument != null ) { argType = { Class.forName( "java.lang.String" ) }; parameter = { argument }; } Method toInvoke; toInvoke = this.getClass().getMethod( methodName, argType); return toInvoke.invoke( this, parameter ); }
Java & Reflection
Function Pointers in Java #2 Inner Classes
Airline Example
import java.util.HashMap; public interface Command { public String execute(String agrument ); } public class AirlineServer implements ServerEngine { public String getCitiesList( ) { blah} public String getLunchMenu( ) { more blah} public String getFlightManifest( String usedHere ) { blah blah} class CitiesCommand implements Command { public String execute(String argument) { return getCitiesList(); } } class LunchCommand implements Command { public String execute(String argument) { return getLunchMenu(); } } class FlightManifestCommand implements Command { public String execute(String argument) { return getFlightManifest(argument); } }
Still in the AirlineServer Class HashMap commands = new HashMap(); { commands.put( "getCitiesList", new CitiesCommand()); commands.put( "getLunchMenu", new LunchCommand()); commands.put( "getFlightManifest", new FlightManifestCommand()); } public void processRequest(InputStream in, OutputStream out, InetAddress clientAddress) throws IOException { ProtocolParser requestData = new ProtocolParser( in ); String request = requestData.getCommand(); String requestParameter = requestData.getParameter; Command clientRequest =(Command) commands.get( request); clientRequest.execute( requestParameter ); } }
Objects as Functions
Using "thin" classes allows us to create objects that are just functions
The object functions can be mapped to strings
Allows us to implement state tables
A bit awkward to use
Objects as States
The Basic Idea
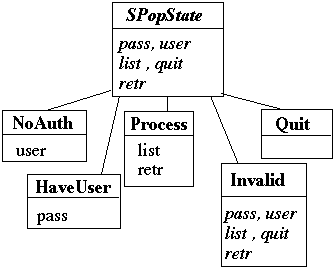
Each method (pass, user, etc.) performs the proper action for the given state and returns the next state
SPopState is abstract state with the default behavior for each method
Server is done with client when we reach the Quit state, so I did not add methods to that state
Strawman Driver Program
class SPopServer implements ServerEngine { public void processRequest(InputStream in, OutputStream out, InetAddress clientAddress) throws IOException { SPopState currentState = new NoAuth(); do { ProtocolParser requestData = new ProtocolParser( in ); String request = requestData.getCommand(); if ( request .startsWith( "PASS" ) ) currentState = currentState.pass(); else if ( request .startsWith( "USER" ) ) currentState = currentState.user(); etc. send response to client } while ( ! currentState instanceof Quit ); } }
Issues
The methods of SPopState and child classes:
CardboardMan Driver Program
class SPopServer implements ServerEngine { public void processRequest(InputStream in, OutputStream out, InetAddress clientAddress) throws IOException { ProtocolParser requestData = new ProtocolParser( in ); String request = requestData.getCommand(); SPopState currentState = new NoAuth(); do { SPopResponse answer = new SPopResponse(); if ( request .startsWith( "PASS" ) ) currentState = currentState.pass( answer ); else if ( request .startsWith( "USER" ) ) currentState = currentState.user( answer ); etc. output.println( answer ); } while ( ! currentState instanceof Quit ); } }
CardboardMan SPOPState
public class SPOPState { public SPOPState USER( other arguments, SPopResponse serverResponse ) { return defaultAction( serverResponse ); } public SPOPState PASS( other arguments, SPopResponse serverResponse ) { return defaultAction( serverResponse ); } public SPOPState LIST( other arguments, SPopResponse serverResponse ) { return defaultAction( serverResponse ); } private SPOPState defaultAction( SPopResponse serverResponse ) { serverResponse.error(); return new Invalid(); } }
Issue - The State of the States How do States get past Information?
The NoAuth state gets the user name
The HaveUser state gets the password
The HaveUser state needs the user name to verify password
But the PASS command from client does not contain user name
The Process state needs user name to get mail messages
SoggyCardboardMan NoAuth
public class NoAuth extends SPOPState { public SPOPState user( some other arguments, SPopResponse serverResponse ) { serverResponse = new SPopResponse.ok(); String userName = get userName from argument list; return new HaveUser( userName ); } }
Now HaveUser object has user name!
Problem with State having States?!(Who is on first?)
Each client request can result in creating a new state object
If a large number of clients connect to a concurrent server at the same time, the creation of all the state objects can become a performance issue
Solution is to create one object per state class and reuse it
If the objects have data fields (data members) then two threads can not use the same object
Solution is to not allow the state classes to have any data fields
So where do we store the user name so other state objects can access it?
Solution is to create a class to store the data needed by all states
Call this class SPopData
What are the responsibilities of SPopData?
TinMan NoAuth
public class NoAuth extends SPOPState { public SPOPState user( some other arguments,SPopData data, SPopResponse serverResponse ) { serverResponse = new SPopResponse.ok(); String userName = get userName from argument list; data.setUserName( userName ); return new HaveUser( ); } }
TinMan SPopServer class SPopServer implements ServerEngine { public void processRequest(InputStream in, OutputStream out, InetAddress clientAddress) throws IOException { SPopState currentState = new NoAuth(); SPopData clientData, do { ProtocolParser requestData = new ProtocolParser( in ); String request = requestData.getCommand(); SPopResponse answer = new SPopResponse(); if ( inputLine.startsWith( "PASS" ) ) currentState = currentState.pass( clientData, answer ); else if ( inputLine.startsWith( "USER" ) ) currentState = currentState.user( clientData, answer ); etc. output.println( answer ); } while ( ! currentState instanceof Quit ); } }
Issue - How to create Just One Object
// Only one object of this class can be created public class NoAuth extends SPOPState { private static NoAuth _instance = null; private NoAuth() { } public static NoAuth getInstance() { if ( _instance == null ) _instance = new NoAuth(); return _instance; } public SPOPState user( some other arguments,SPopData data, SPopResponse serverResponse ) { serverResponse = new SPopResponse.ok(); String userName = get userName from argument list; data.setUserName( userName ); return new HaveUser( ); } } class Program { public void aMethod() { X = NoAuth.getInstance(); } }
The Interesting Questions
Who does the actual work?